
Although one district after another has been declared fully literate, Kathmandu, the capital city of the country, is yet to be declared fully literate. A district where at least 95 per cent of people in the 15-60 age group are literate is considered fully literate. It does not require cent per cent literacy for a district to be declared fully literate.

It is heartening to note that the government has adopted a policy of declaring a particular district fully literate after the district has fulfilled the required criteria. In this regard, educational institutions, NGOs, civil society organisations and other stakeholders like teachers, students, parents and political parties should act in tandem to materialise the Literate Nepal campaign. The government needs cooperation, coordination and synergy from other sectors, too. The efforts of the government alone are not adequate. As a matter of fact, making the country literate is a daunting task. The concept paper is a basic guideline for formulating policy and norms related to making the country literate by 2030 in line with the international concept of education for all. Accordingly, the government announced the concept paper Literate Nepal Year 2019 on December 31, 2018. Nepal, on its part, is trying to fulfil, among others, the education-related goal of the SDGs. Now the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) have tried to achieve the goal of education. Under the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), every country was required to impart quality education to its people and make everyone literate by the year 2015 but the goal could not be achieved. So, non-formal education encourages self-employment, enabling to deal with unemployment and poverty issues. This will enable them to enhance their skills for their livelihoods as well as for their socioeconomic development. The non-formal education scheme not only makes people literate but also imparts technical and vocational training to them, which is one of its beautiful aspects. So the scheme welcomes everyone from children to the elderly. The non-formal education scheme does not discriminate against anybody in terms of caste, gender, age, religion, language and even disabilities. The non-formal education scheme is like an open school. The non-formal education scheme aims at imparting education equivalent to formal education through the open school system, providing continuing education for people with different skills and educational levels, embarking on an oral literacy campaign for awareness among people and imparting education equivalent to higher-level education through the open university system, among others. In fact, the non-formal education scheme focuses on literacy and technical and vocational skill enhancement so that poor and underprivileged people can set themselves on their feet for a decent living. However, usually no degree or certificate is awarded to participants at the end of the session. Moreover, the non-formal education system adopts a participatory approach to learning. There is no age bar but it will be easier to segregate participants into homologous groups.
#Non formal education free#
Non-formal education may be free or just a nominal fee may be charged to participants. Likewise, there is no structured course or curriculum. The time can be fixed as per the convenience of participants. Non-formal education is well-planned but does not follow the school system. Non-formal education differs from informal education and formal education. The non-formal education scheme is directed at certain targeted groups like illiterate adults, women and youth out-of-school children and school dropouts and underprivileged people like Dalits, marginalised farmers and workers.
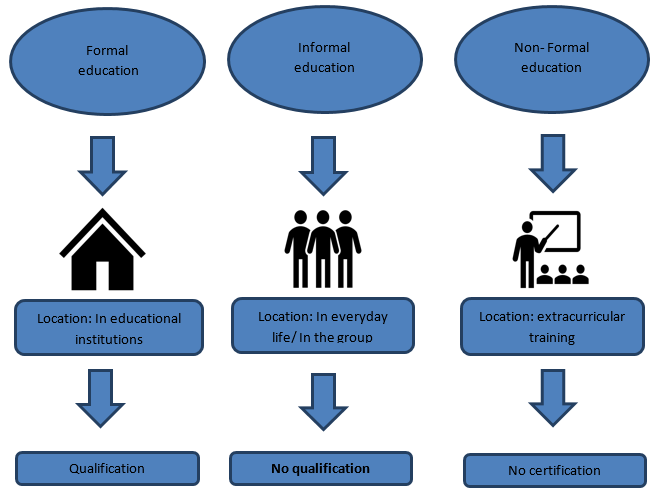
Non-formal education is basically concerned with literacy, post-literacy and awareness-raising programmes with a focus on continuing education, lifelong education, skill development and income generation. To institutionalise non-formal education, it was even encapsulated in the first five-year periodic plan (1956-1961 AD).

In fact, without education, national development cannot be conceived of. With the dawn of democracy, education was given prominence and made part of national development. NON-formal education began in Nepal in 1951 AD, the year when the country was freed from the clutches of the Rana regime through the joint efforts of King Tribhuvan and the Nepalis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
